Multi UAV Task Assignment and Path Planning
Metaheuristic Optimization Techniques for Multi-Cooperative Systems
In this project, we study multiple optimisation techniques to tackle the task assignment and path planning problem for multi Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs).
This Mutli UAV Target Assignment and Path Planning problem, abbreviated as MUTAPP, is considered an NP-hard problem (Non-deterministic Polynomial time) and can be described as a Multi Travelling Salesman Problem (MTSP).
We encounter solutions such as Simulated Annealing (SA), Genetic Algorithm (GA), Hybrid Ant Colony Optimisation and Whale Optimisation Algorithm (H-ACO-WOA), and Hybrid ACO and Dragonfly Algorithm (H-ACO-DA).
The project is implemented in Python and the results are visualised using the Matplotlib library.
Problem Description
The MUTAPP problem is a multi-agent optimisation problem where a set of UAVs are tasked to visit a set of targets. The targets are assumed to be static and the UAVs are assumed to be identical. The UAVs are assumed to have a limited battery life and the targets are assumed to have a limited lifetime. The objective is to minimise the total cost of the mission, which is the sum of the cost of the UAVs and the cost of the targets.
The cost of the UAVs is the sum of the distance travelled by each UAV and the cost of the targets is the sum of the time each target is visited by a UAV.
Solution Approaches
We consider four different approaches to solve the MUTAPP problem:
- Simulated Annealing (SA)
- Genetic Algorithm (GA)
- Hybrid Ant Colony Optimisation and Whale Optimisation Algorithm (H-ACO-WOA)
- Hybrid ACO and Dragonfly Algorithm (H-ACO-DA)
Simulated Annealing (SA)
Simulated Annealing (SA) is a probabilistic technique for approximating the global optimum of a given function. It is often used to find good solutions to combinatorial optimisation problems.
The algorithm starts with an initial solution and then iteratively improves it by making small changes to the solution. The changes are accepted if they improve the solution, but are also accepted with a certain probability if they make the solution worse. This probability decreases as the algorithm progresses, which means that the algorithm is less likely to accept changes that make the solution worse as the algorithm progresses.
Genetic Algorithm (GA)
Genetic Algorithm (GA) is a search heuristic that is inspired by the process of natural selection. It is commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimisation and search problems by relying on bio-inspired operators such as mutation, crossover and selection.
The algorithm starts by initialising a population of candidate solutions to the problem. It then evaluates the fitness of each candidate solution, which is used to determine how likely a candidate solution is to be selected for reproduction. The fitter solutions are more likely to be selected for reproduction, which means that the fitter solutions are more likely to be passed on to the next generation of the algorithm.
Hybrid Ant Colony Optimisation and Whale Optimisation Algorithm (H-ACO-WOA)
Ant Colony Optimisation (ACO) is a probabilistic technique for solving combinatorial optimisation problems. It is inspired by the foraging behaviour of real ants and is often used to find good solutions to the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP).
The algorithm starts by initialising a set of candidate solutions to the problem. It then evaluates the fitness of each candidate solution, which is used to determine how likely a candidate solution is to be selected for reproduction. The fitter solutions are more likely to be selected for reproduction, which means that the fitter solutions are more likely to be passed on to the next generation of the algorithm.
Whale Optimisation Algorithm (WOA) is a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the hunting behaviour of whales. It is commonly used to find good solutions to continuous optimisation problems.
The algorithm starts by initialising a population of candidate solutions to the problem. It then evaluates the fitness of each candidate solution, which is used to determine how likely a candidate solution is to be selected for reproduction. The fitter solutions are more likely to be selected for reproduction, which means that the fitter solutions are more likely to be passed on to the next generation of the algorithm.
Hybrid ACO and Dragonfly Algorithm (H-ACO-DA)
Ant Colony Optimisation (ACO) is a probabilistic technique for solving combinatorial optimisation problems. It is inspired by the foraging behaviour of real ants and is often used to find good solutions to the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP).
The algorithm starts by initialising a set of candidate solutions to the problem. It then evaluates the fitness of each candidate solution, which is used to determine how likely a candidate solution is to be selected for reproduction. The fitter solutions are more likely to be selected for reproduction, which means that the fitter solutions are more likely to be passed on to the next generation of the algorithm.
Dragonfly Algorithm (DA) is a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the hunting behaviour of dragonflies. It is commonly used to find good solutions to continuous optimisation problems.
The algorithm starts by initialising a population of candidate solutions to the problem. It then evaluates the fitness of each candidate solution, which is used to determine how likely a candidate solution is to be selected for reproduction. The fitter solutions are more likely to be selected for reproduction, which means that the fitter solutions are more likely to be passed on to the next generation of the algorithm.
Results
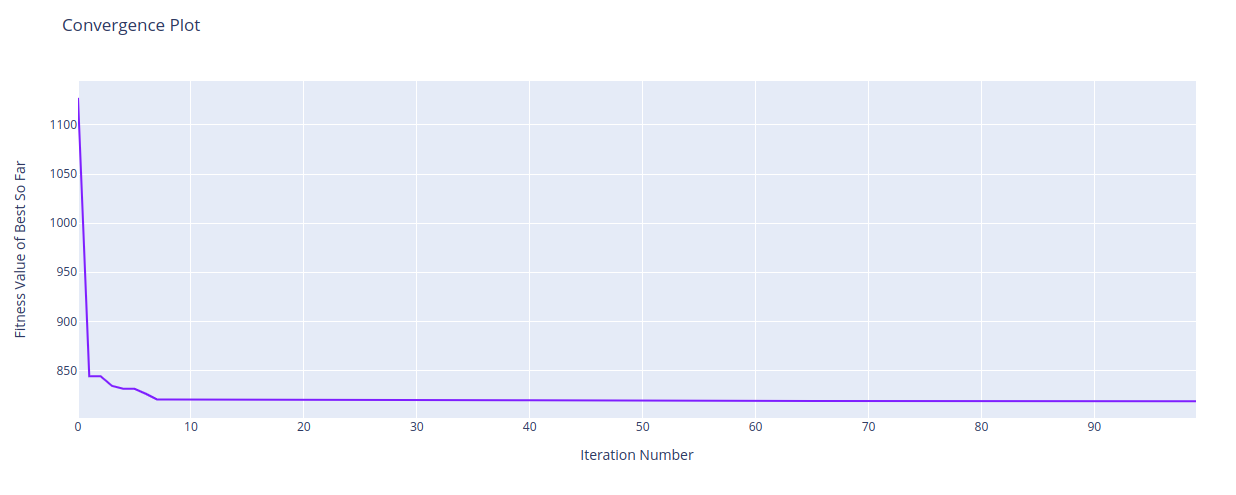
The results of the project are visualised using the Matplotlib library.
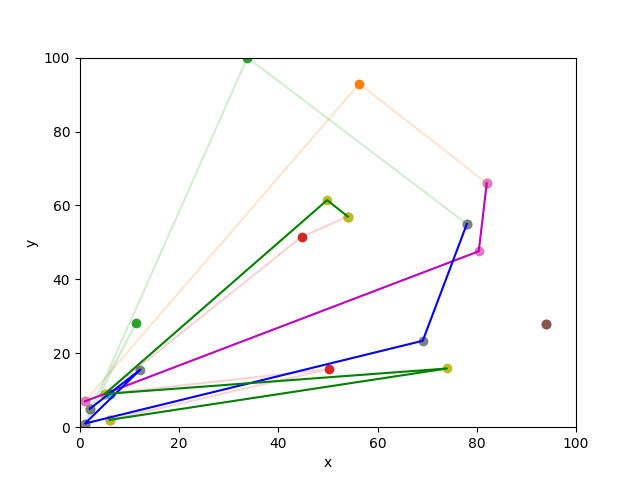
The following figure shows the results of the Simulated Annealing (SA) approach.
The following figure shows the results of the Genetic Algorithm (GA) approach.
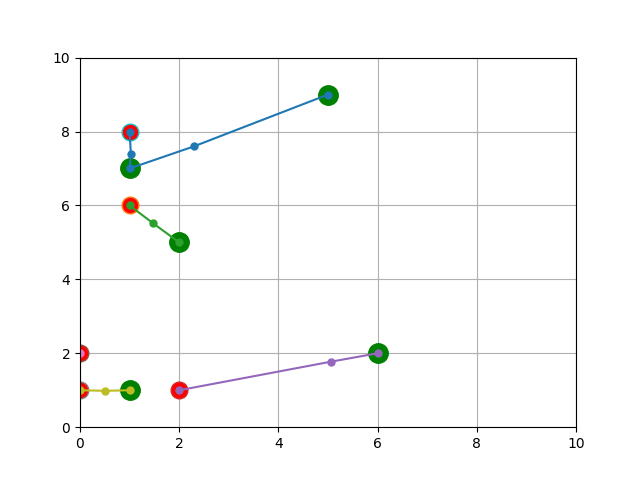
The following figure shows the results of the Hybrid Ant Colony Optimisation and Whale Optimisation Algorithm (H-ACO-WOA) approach.
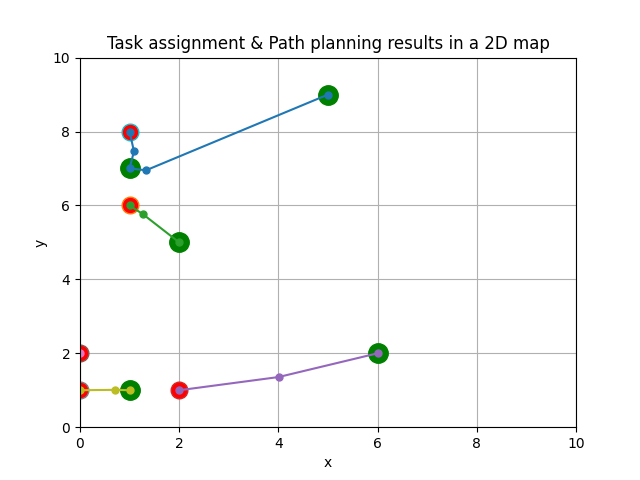
The following figure shows the results of the Hybrid ACO and Dragonfly Algorithm (H-ACO-DA) approach.
Conclusion
The project has demonstrated how to solve the Multi UAV Task Assignment and Path Planning (MUTAPP) problem using different approaches. The project has also demonstrated how to visualise the results of the different approaches.
The project has demonstrated how to solve the Multi UAV Task Assignment and Path Planning (MUTAPP) problem using different approaches. The project has also demonstrated how to visualise the results of the different approaches.
References
- Multi UAV Task Assignment and Path Planning (MUTAPP) Problem
- Simulated Annealing (SA)
- Genetic Algorithm (GA)
- Ant Colony Optimisation (ACO)
- Whale Optimisation Algorithm (WOA)
- Dragonfly Algorithm (DA)
- Matplotlib
- Python
- Jupyter Notebook
Source Code
The source code for the project is available on GitHub.